PuTTYgen currently supports three types of key: An RSA key for use with the SSH-1 protocol.An RSA key for use with the SSH-2 protocol.A DSA key for use with the SSH-2 protocol.The SSH-1 protocol only supports RSA keys; if you will be connectingusing the SSH-1 protocol, you must select the first key type or yourkey will be completely useless.The SSH-2 protocol supports more than one key type. Putty key generator ssh-2 rsa.
This class provides the functionality of a secret (symmetric) key generator.Step6: As we know S-DES has two round and for that we also need two keys, one key we generate in the above steps (step 1 to step 5). Now we need to generate a second bit and after that we will move to encrypt the plain text or message. It is simple to generate.
- Key Generation. The round-key generator creates sixteen 48-bit keys out of a 56-bit cipher key. The process of key generation is depicted in the following illustration − The logic for Parity drop, shifting, and Compression P-box is given in the DES description. DES Analysis. The DES satisfies both the desired properties of block cipher.
- Feb 27, 2017 This feature is not available right now. Please try again later.
- Using the KeyGenerator class and showing how to create a SecretKeySpec from an encoded key. AES Key generator: 36.2.3. Tampered message, plain encryption, AES in CTR mode: 36.2.4. Tampered message, encryption with digest, AES in CTR mode: 36.2.5. Tampered message with HMac, encryption with AES in CTR mode: 36.2.6. AES wraps RSA.
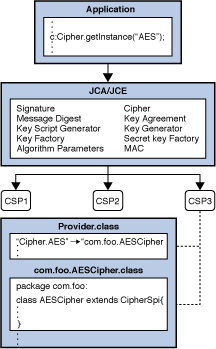
Key generators are constructed using one of the getInstance class methods of this class.
KeyGenerator objects are reusable, i.e., after a key has been generated, the same KeyGenerator object can be re-used to generate further keys.
Ms office 2010 serial. There are two ways to generate a key: in an algorithm-independent manner, and in an algorithm-specific manner. The only difference between the two is the initialization of the object:
- Algorithm-Independent Initialization
All key generators share the concepts of a keysize and a source of randomness. There is an
initmethod in this KeyGenerator class that takes these two universally shared types of arguments. There is also one that takes just akeysizeargument, and uses the SecureRandom implementation of the highest-priority installed provider as the source of randomness (or a system-provided source of randomness if none of the installed providers supply a SecureRandom implementation), and one that takes just a source of randomness.Since no other parameters are specified when you call the above algorithm-independent
initmethods, it is up to the provider what to do about the algorithm-specific parameters (if any) to be associated with each of the keys. - Algorithm-Specific Initialization
For situations where a set of algorithm-specific parameters already exists, there are two
initmethods that have anAlgorithmParameterSpecargument. One also has aSecureRandomargument, while the other uses the SecureRandom implementation of the highest-priority installed provider as the source of randomness (or a system-provided source of randomness if none of the installed providers supply a SecureRandom implementation).
In case the client does not explicitly initialize the KeyGenerator (via a call to an init method), each provider must supply (and document) a default initialization.
Des Key Generation In Java Download

Every implementation of the Java platform is required to support the following standard KeyGenerator algorithms with the keysizes in parentheses:
Des Key Generation In Java 10
- AES (128)
- DES (56)
- DESede (168)
- HmacSHA1
- HmacSHA256