Mar 30, 2020 If you want to delete the current Instance ID and immediately use Firebase services with a new, independent ID, use one of the Client APIs above to handle the deletion. Disable Instance ID generation Services that use Instance IDs automatically generate a new ID when they're initialized in an app that doesn't currently have one. If you would like to have a special key for use in a server, then you can generate one by navigating to the firebase console for your project, selecting the gear in the top left hand corner and selecting project settings. Then select service accounts at the top. Then select Firebase Admin SDK and then generate new private key. Hope this helps!
- Firebase Auto Generated New Api Key In Minecraft
- Firebase Auto Generated New Api Keys
- Firebase Auto Generated New Api Key Download
Released:
Python interface to the Google's Firebase REST APIs
Project description
Author: Joe Tilsed Created: 09.02.2019 Last Updated: 10.02.2019
Python interface to the Google's Firebase REST APIs
Installation
Python Version
Firebase was written for python 3 and above and will not work correctly with python 2.
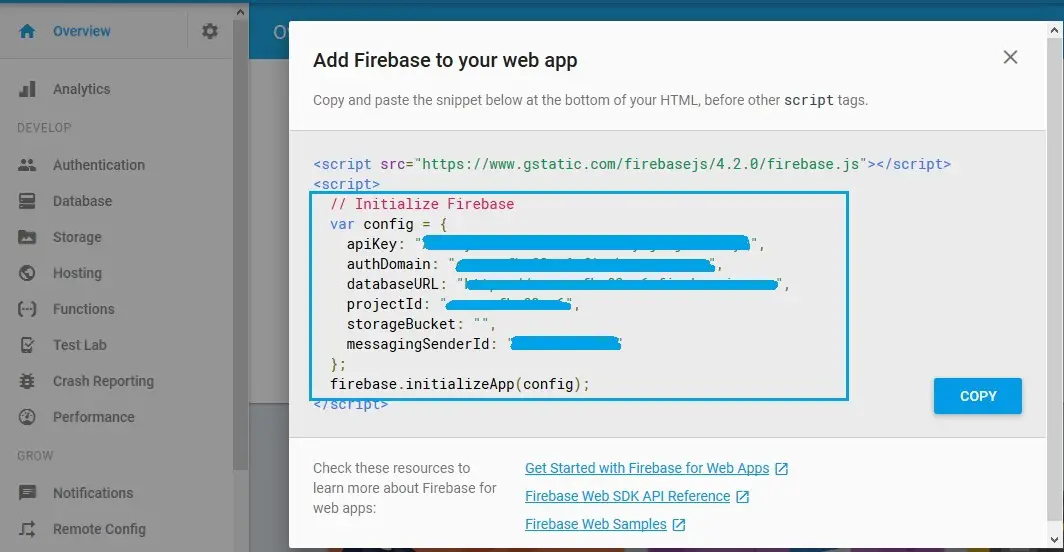
Add Firebase to your Application
Your Google's Firebase configuration data can be found on Firebase > Settings > Project Settings Scroll to bottom > Add to web app > config
For use with only user based authentication we can create the following configuration:
You can optionally add a service account credential to ourconfiguration that will allow your server to authenticate with Firebase as an admin and disregard any security rules.
Adding a service account will authenticate as an admin by default for all database queries, check out theAuthentication documentation for how to authenticate users.
Use Services
A firebase app can use multiple Firebase services.
firebase.auth() - Authentication
firebase.database() - Database
firebase.storage() - Storage
Check out the documentation for each service for further details.
Authentication
The sign_in_with_email_and_password() method will return user data including a token you can use to adhere to security rules.
Each of the following methods accepts a user token: get(), push(), set(), update(), remove() and stream().
Token expiry
A user's idToken expires after 1 hour, so be sure to use the user's refreshToken to avoid stale tokens.
Custom tokens
You can also create users using custom tokens, for example:
You can also pass in additional claims.
You can then send these tokens to the client to sign in, or sign in as the user on the server.
Manage Users
Creating users
Note: Make sure you have the Email/password provider enabled in your Firebase dashboard under Auth -> Sign In Method.
Verifying emails
Sending password reset emails
Get account information
Refreshing tokens
Database
You can build paths to your data by using the child() method.
Save Data
push
To save data with a unique, auto-generated, timestamp-based key, use the push() method.
set
To create your own keys use the set() method. The key in the example below is 'Joe'.
update
To update data for an existing entry use the update() method.
remove
To delete data for an existing entry use the remove() method.
multi-location updates
You can also perform multi-location updates with the update() method.
To perform multi-location writes to new locations we can use the generate_key() method.
Generate git ssh key ubuntu. This post will be pretty straightforward and will cover Windows, Mac, and Linux, so if you don’t know how to do it already, read on.
Retrieve Data
val
Queries return a FirebaseResponse object. Calling val() on these objects returns the query data.
key

Calling key() returns the key for the query data.
each
Returns a list of objects on each of which you can call val() and key().
get
To return data from a path simply call the get() method.
shallow
To return just the keys at a particular path use the shallow() method.
Note: shallow() can not be used in conjunction with any complex queries.
streaming
You can listen to live changes to your data with the stream() method.
You should at least handle put and patch events. Refer to 'Streaming from the REST API' for details.
You can also add a stream_id to help you identify a stream if you have multiple running:
close the stream
Complex Queries
Queries can be built by chaining multiple query parameters together.
This query will return the first three users ordered by name.
order_by_child
We begin any complex query with order_by_child().
This query will return users ordered by name.
equal_to
Return data with a specific value.
This query will return users with a score of 10.
start_at and end_at
Specify a range in your data.
This query returns users ordered by score and with a score between 3 and 10.
limit_to_first and limit_to_last
Limits data returned.
This query returns the first five users ordered by score.
order_by_key
When using order_by_key() to sort your data, data is returned in ascending order by key.
order_by_value
When using order_by_value(), children are ordered by their value.
Storage
The storage service allows you to upload images to Firebase.
child
Just like with the Database service, you can build paths to your data with the Storage service.
Firebase Auto Generated New Api Key In Minecraft
put
The put method takes the path to the local file and an optional user token.
Share the flashcard by embedding it on your website or blog Network+ Guide to Networks, Chapter 12, Part 2 » ProProfs Flashcard Software. An encryption key generation and management scheme used by 802.11i example.
download
The download method takes the path to the saved database file and the name you want the downloaded file to have.
get_url
The get_url method takes the path to the saved database file and returns the storage url.
Helper Methods
generate_key
db.generate_key() is an implementation of Firebase's key generation algorithm.
See multi-location updates for a potential use case.
sort
Sometimes we might want to sort our data multiple times. For example, we might want to retrieve all articles written between acertain date then sort those articles based on the number of likes.
Currently the REST API only allows us to sort our data once, so the sort() method bridges this gap.
Common Errors
Index not defined
Indexing is not enabled for the database reference.
# That's all folks..
Firebase Auto Generated New Api Keys
Release historyRelease notifications
3.0.1
3.0.0
2.2.0
2.1.4
2.1.3
2.1.2
2.1.1
2.1.0
2.0.1
2.0.0
1.0.1
1.0.0
Download files
Firebase Auto Generated New Api Key Download
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
| Filename, size | File type | Python version | Upload date | Hashes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filename, size firebase-3.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (18.0 kB) | File type Wheel | Python version py3 | Upload date | Hashes |
Hashes for firebase-3.0.1-py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest |
|---|---|
| SHA256 | 39f7a149bef90735a17fddda30cab3cb24b03e40ab221c12e1217ff0cfd38203 |
| MD5 | 0356979a0e336dc947769a0d3a6f21ad |
| BLAKE2-256 | f8336b2a24e349563f2d279ccc8321f26a9c0d6d2f8205adb68f3046c3ec7a89 |