Important: This example is intended to provide general guidance to IT professionals who are experienced with SSL requirements and configuration. The procedure described in this article is just one of many available methods you can use to generate the required files. The process described here should be treated as an example and not as a recommendation.
Ubuntu: Creating a trusted CA and SAN certificate using OpenSSL There are numerous articles I’ve written where a certificate is a prerequisite for deploying a piece of infrastructure. This article will guide you through creating a trusted CA (Certificate Authority), and then using that to sign a server certificate that supports SAN ( Subject. May 07, 2019 Facebook Twitter Gmail LinkedIn SSL certificates are cool. They will be used more and more. This tutorial should be used only on development and/or test environments! For a production environment please use the already trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). This key & certificate will be used to sign other self signed certificates. That will be covered.
When you configure Tableau Server to use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption, this helps ensure that access to the server is secure and that data sent between Tableau Server and Tableau Desktop is protected.
Looking for Tableau Server on Linux? See Example: SSL Certificate - Generate a Key and CSR.
Tableau Server uses Apache, which includes OpenSSL. You can use the OpenSSL toolkit to generate a key file and Certificate Signing Request (CSR) which can then be used to obtain a signed SSL certificate.
Steps to generate a key and CSR
To configure Tableau Server to use SSL, you must have an SSL certificate. To obtain the SSL certificate, complete the steps:
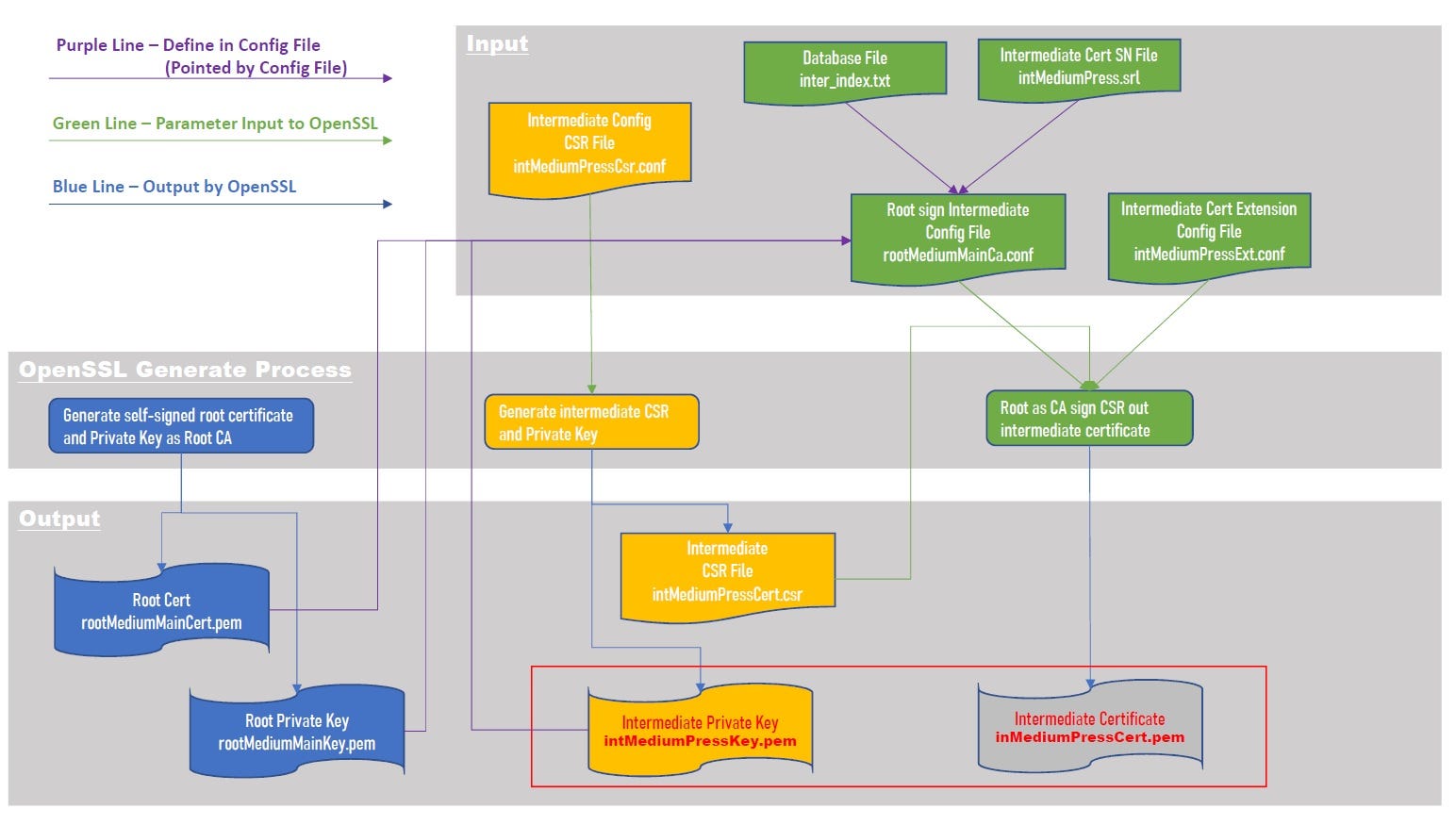
- Generate a key file.
- Create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
- Send the CSR to a certificate authority (CA) to obtain an SSL certificate.
- Use the key and certificate to configure Tableau Server to use SSL.
You can find additional information on the SSL FAQ page on the Apache Software Foundation website.
Configure a certificate for multiple domain names
Tableau Server allows SSL for multiple domains. To set up this environment, you need to modify the OpenSSL configuration file, openssl.conf, and configure a Subject Alternative Name (SAN) certificate on Tableau Server. See For SAN certificates: modify the OpenSSL configuration file below.
Set the OpenSSL configuration environment variable (optional)
To avoid using the -config argument with every use of openssl.exe, you can use the OPENSSL_CONF environment variable to ensure that the correct configuration file is used and all configuration changes made in subsequent procedures in this article produce expected results (for example, you must set the environment variable to add a SAN to your certificate).
Open the Command Prompt as an administrator, and run the following command:
set OPENSSL_CONF=c:Program FilesTableauTableau Serverpackagesapache.<version_code>confopenssl.cnf
Notes:
When setting the Open SSL configuration environment variable, do not enclose the file path with quotation marks.
If you are using a 32-bit version of Tableau Server on a 64-bit computer, run the
set OPENSSL_CONF=c:Program Files (x86)TableauTableau Serverpackagesapache.<version_code>confopenssl.cnfcommand instead.
Generate a key
Generate a key file that you will use to generate a certificate signing request.
Open the Command Prompt as an administrator, and navigate to the Apache directory for Tableau Server. For example, run the following command:
High Rank Key Quests HR4 to HR7 is High Rank! These quests will be more difficult, you may start at a random location on the map and you'll have to bring your own supplies.4-Star Multiplayer Key Quests Quest NameTargetSwining into ActionBug AppetitShells of SteelBirds of a Feather&Urgent Quest: A Plesioth in the Misty Peaks5-Star Multiplayer Key Quests Quest NameTargetThe Intelligent MalfestioSerpentine SambaFin FinderWorst. Ever!You Caught This? I Caught ThisUrgent Quest: A Bewitching DanceUrgent Quest: The Unshakable Mountain GodNote: Completing The Unshakable Mountain God quest will increase the level of scouted Palicos and add Wyvern Amber Ale6-Star Multiplayer Key Quests Quest NameTargetThe Lightning CrownBug BuffetMaster of the Molten DeepDuel in the Volcanic HollowFor Whom the Gong TollsUrgent Quest: Seer of Swords7-Star Multiplayer Key Quests Quest NameTargetStop thhe WheelA Gathering of Wyverns&A Song of White a Lapis&A Cold Set of Armor&Rocked and RolledHammer vs. Monster hunter generations story key quests free.
cd C:Program FilesTableauTableau Serverpackagesapache.<version_code>binRun the following command to create the key file:
openssl.exe genrsa -out <yourcertname>.key 4096Note: This command uses a 4096-bit length for the key. You should choose a bit length that is at least 2048 bits because communication encrypted with a shorter bit length is less secure. If a value is not provided, 512 bits is used.
Create a certificate signing request to send to a certificate authority
Use the key file you created in the procedure above to generate the certificate signing request (CSR). You send the CSR to a certificate authority (CA) to obtain a signed certificate.
Important: If you want to configure a SAN certificate to use SSL for multiple domains, first complete the steps in For SAN certificates: modify the OpenSSL configuration file below, and then return to here to generate a CSR.
Run the following command to create a certificate signing request (CSR) file:
openssl.exe req -new -key yourcertname.key -out yourcertname.csrIf you did not set the OpenSSL configuration environment variable,
OPENSSL_CONF, you might see either of the following messages:An error message about the config information being unable to load. In this case, retype the command above with the following parameter:
-config .confopenssl.cnf.A warning that the
/usr/local/ssldirectory cannot be found. This directory does not exist on Windows, and you can simply ignore this message. The file is created successfully.
To set an OpenSSL configuration environment variable, see Set the OpenSSL configuration environment variable (optional) section in this article.
When prompted, enter the required information.
Note: For Common Name, type the Tableau Server name. The Tableau Server name is the URL that will be used to reach the Tableau Server. For example, if you reach Tableau Server by typing
tableau.example.comin the address bar of your browser, thentableau.example.comis the common name. If the common name does not resolve to the server name, errors will occur when a browser or Tableau Desktop tries to connect to Tableau Server.
Send the CSR to a certificate authority to obtain an SSL certificate
Send the CSR to a commercial certificate authority (CA) to request the digital certificate. For information, see the Wikipedia article Certificate authority and any related articles that help you decide which CA to use.

Use the key and certificate to configure Tableau Server
When you have both the key and the certificate from the CA, you can configure Tableau Server to use SSL. For the steps, see Configure External SSL.
For SAN certificates: modify the OpenSSL configuration file
In a standard installation of OpenSSL, some features are not enabled by default. To use SSL with multiple domain names, before you generate the CSR, complete these steps to modify the openssl.cnf file.
Open Windows Explorer and browse to the Apache conf folder for Tableau Server.
For example:
C:Program FilesTableauTableau Server<version_code>apacheconfOpen openssl.cnf in a text editor, and find the following line:
req_extensions = v3_reqThis line might be commented out with a hash sign (#) at the beginning of the line.
If the line is commented out, uncomment it by removing the # and space characters from the beginning of the line.
Move to the [ v3_req ] section of the file. The first few lines contain the following text:
# Extensions to add to a certificate request
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEnciphermentAfter the keyUsage line, insert the following line:
subjectAltName = @alt_namesWhich tag specifies a key-pair generator field in a form 1.If you’re creating a self-signed SAN certificate, do the following to give the certificate permission to sign the certificate:
Add the
cRLSignandkeyCertSignto the keyUsage line so it looks like the following:keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment, cRLSign, keyCertSignAfter the keyUsage line, add the following line:
subjectAltName = @alt_names
In the [alt_names] section, provide the domain names you want to use with SSL.
DNS.1 = [domain1]
DNS.2 = [domain2]
DNS.3 = [etc]The following image shows the results highlighted, with placeholder text that you would replace with your domain names.
Save and close the file.
Complete the steps in Create a certificate signing request to send to a certificate authority section, above.
Additional information
If you prefer to use a different version of OpenSSL, you can download it from Open SSL for Windows.
6.3.7 Creating SSL Certificates and Keys Using openssl
This section describes how to use the openssl command to set up SSL certificate and key files for use by MySQL servers and clients. The first example shows a simplified procedure such as you might use from the command line. The second shows a script that contains more detail. The first two examples are intended for use on Unix and both use the openssl command that is part of OpenSSL. The third example describes how to set up SSL files on Windows.
Whatever method you use to generate the certificate and key files, the Common Name value used for the server and client certificates/keys must each differ from the Common Name value used for the CA certificate. Otherwise, the certificate and key files will not work for servers compiled using OpenSSL. A typical error in this case is:
Example 1: Creating SSL Files from the Command Line on Unix
The following example shows a set of commands to create MySQL server and client certificate and key files. You will need to respond to several prompts by the openssl commands. To generate test files, you can press Enter to all prompts. To generate files for production use, you should provide nonempty responses.
After generating the certificates, verify them:
Now you have a set of files that can be used as follows:
ca.pem: Use this as the argument to--ssl-caon the server and client sides. (The CA certificate, if used, must be the same on both sides.)server-cert.pem,server-key.pem: Use these as the arguments to--ssl-certand--ssl-keyon the server side.client-cert.pem,client-key.pem: Use these as the arguments to--ssl-certand--ssl-keyon the client side.
To use the files for SSL connections, see Section 6.3.6.4, “Configuring MySQL to Use Secure Connections”.
Example 2: Creating SSL Files Using a Script on Unix
Here is an example script that shows how to set up SSL certificate and key files for MySQL. After executing the script, use the files for SSL connections as described in Section 6.3.6.4, “Configuring MySQL to Use Secure Connections”.
Example 3: Creating SSL Files on Windows
Download OpenSSL for Windows if it is not installed on your system. An overview of available packages can be seen here:
Choose the Win32 OpenSSL Light or Win64 OpenSSL Light package, depending on your architecture (32-bit or 64-bit). The default installation location will be C:OpenSSL-Win32 or C:OpenSSL-Win64, depending on which package you downloaded. The following instructions assume a default location of C:OpenSSL-Win32. Modify this as necessary if you are using the 64-bit package.
If a message occurs during setup indicating '..critical component is missing: Microsoft Visual C++ 2008 Redistributables', cancel the setup and download one of the following packages as well, again depending on your architecture (32-bit or 64-bit):
Visual C++ 2008 Redistributables (x86), available at:
Visual C++ 2008 Redistributables (x64), available at:
After installing the additional package, restart the OpenSSL setup procedure.
Openssl Generate Ca Certificate And Key
During installation, leave the default C:OpenSSL-Win32 as the install path, and also leave the default option 'Copy OpenSSL DLL files to the Windows system directory' selected.
When the installation has finished, add C:OpenSSL-Win32bin to the Windows System Path variable of your server:
On the Windows desktop, right-click the My Computer icon, and select Properties.
Select the Advanced tab from the System Properties menu that appears, and click the button.
Under System Variables, select Path, then click the button. The Edit System Variable dialogue should appear.
Add
';C:OpenSSL-Win32bin'to the end (notice the semicolon).Press OK 3 times.
Check that OpenSSL was correctly integrated into the Path variable by opening a new command console (Start>Run>cmd.exe) and verifying that OpenSSL is available:
Depending on your version of Windows, the preceding path-setting instructions might differ slightly.
After OpenSSL has been installed, use instructions similar to those from from Example 1 (shown earlier in this section), with the following changes:
Change the following Unix commands:
On Windows, use these commands instead:
When a
'character is shown at the end of a command line, this'character must be removed and the command lines entered all on a single line.
Openssl Generate Ca Cert And Key Download
After generating the certificate and key files, to use them for SSL connections, see Section 6.3.6.4, “Configuring MySQL to Use Secure Connections”.