Connect to a server by using SSH on Linux or Mac OS X
- Command To Generate Ssh Key On Mac Free
- Ssh Key Generator Mac
- Mac Ssh Key Location
- How To Generate Ssh Key On Mac
- Command To Generate Ssh Key On Mac Download
This article provides steps for connecting to a cloud server froma computer running Linux® or MacOS® X by using Secure Shell (SSH).It also discusses generating an SSH key and adding a public key tothe server.
Introduction
SSH is a protocol through which you can access your cloud server and runshell commands. You can use SSH keys to identify trusted computers withoutthe need for passwords and to interact with your servers.
Oct 06, 2018 First thing that you need to do on your macOS machine is to create a directory that will store your SSH keys. Then you will generate a public and private key for your account, launch the Terminal and punch in some commands: Create a.ssh Directory. Change to the home directory. Cd / Create a SSH directory name.ssh and move into it.
SSH is encrypted with Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), which makes it difficultfor these communications to be intercepted and read.
Note: Many of the commands in this article must be run on your localcomputer. The default commands listed are for the Linux command line orMacOS X Terminal. To make SSH connections from Windows®, you can use a clientsimilar to the free program, PuTTY.To generate keys, you can use a related program, PuTTYGen.
Log in
Using the Internet Protocol (IP) address and password for your cloud server, log in byrunning the following ssh command with username@ipaddress as the argument:
The system prompts you to enter the password for the account to which you’reconnecting.
Remote host identification
If you rebuilt your cloud server, you might get the following message:
One of the security features of SSH is that when you log in to a cloudserver, the remote host has its own key that identifies it. When you tryto connect, your SSH client checks the server’s key against any keysthat it has saved from previous connections to that IP address. After yourebuild a cloud server, that remote host key changes, so your computerwarns you of possibly suspicious activity.
To ensure the security of your server, you canuse the web console in the Cloud Control Panel to verify your server’s new key.If you’re confident that you aren’t being spoofed, you can skip thatstep and delete the record of the old SSH host key as follows:
On your local computer, edit the SSH known_hosts file and remove anylines that start with your cloud server’s IP address.
Note: Use the editor of your choice, such as nano on Debian or theUbuntu operating systemor vi on RPM or CENTOS servers. For simplicity, this article just uses nano. If you prefer to use vi,substitute vi for nano in the edit commands.For more on using nano, seehttps://support.rackspace.com/how-to/modify-your-hosts-file/.
If you are not using Linux or MacOS X on your local computer, thelocation of the known_hosts file might differ. Refer to your OS forinformation about the file location. PuTTY on Windows gives you theoption to replace the saved host key.
Generate a new SSH key pair
You can secure SSH access to your cloud server against brute forcepassword attacks by using a public-private key pair. A public key is placed onthe server and a matching private key is placed on your local computer. If youconfigure SSH on your server to accept only connections using keys,then no one can log in by using just a password. Connecting clientsare required to use a private key that has a public key registered onthe server. For more on security, reviewLinux server security best practices.
Use the following steps to generate an SSH key pair:
Run the following command using your email address as a label.Substitute your email address for
[email protected]inthe command.A message indicates that your public-private RSA key pair isbeing generated.
At the prompt, press Enter to use the default location or entera file in which to save the key and press Enter.
If you want the additional security of a password for the key pair,enter a passphraseand press Enter. If you don’t want to use a passwordwith the key pair, press Enter to continue without setting one.
Your key pair is generated, and the output looks similar to the following example:
Optionally, add your new key to the local ssh-agent file to enableSSH to find your key without the need to specify its location everytime that you connect:
You can use an SSH configuration shortcut instead of the ssh-agent fileby following the instructions in the Shortcut configuration sectionlater in this article.
Add the public key to your cloud account
To make it easy to add your key to new cloud servers that you create,upload the public key to your cloud account by following these steps:
- Log in to the Cloud Control Panel.
- In the top navigation bar, click Select a Product > Rackspace Cloud.
- Select Servers > SSH Keys.
- Click Add Public Key.
- Enter a key name, such as Work Laptop, to remind you which computer this key is for.
- Select the region for which you want to store the public key. Tostore your key in multiple regions, repeat these steps foreach region. The key must reside in the same region as the server.
Paste the contents of the id_rsa.pub file that you created intothe Public Key field. You can get the file contents by eitheropening the file in a text editor or by running the followingcommand:
- Click Add Public Key.
If you want to add the key manually, instead of by using the Control Panel, reviewLinux server security best practicesand use the following command:
Create a new server by using a stored key
When you create a new cloud server, you can add a stored key to the newserver.
On the Create Server page, expand the Advanced Options section.
From the SSH Key menu, select your key from the list.
If you don’t see a stored key in the list, you can perform one of the following actions:
- Switch the region for the new server to the region where you have stored the SSH key.
- Repeat the steps in the preceding section, Add the public key to your cloud account,to add the key to the region in which you want to create the new server.
Add the key to an existing server
You can’t use the Cloud Control Panel to add a public key to anexisting server. Follow these steps to add the key manually:
On your cloud server, create a directory named .ssh in the homefolder of the user that you connect to by using SSH.
Create or edit the authorized_keys file and add your public key tothe list of authorized keys by using the following command:
A key is all on one line, so ensure that the key isn’t broken byline breaks. You can have multiple keys in the authorized_keysfile, with one key per line.
Set the correct permissions on the key by using the following commands:
If you have any issues and need to fix permissions issues, run the following comand:
After you have added the public key to the authorized_keys, you can make an SSHconnection by using your key pair instead of the account password.
Shortcut configuration
Use the following instructions to set up a connection shortcut by creating a~/.ssh/config file on your local computer and adding your server and keydetails to it.
Using a text editor, add the following text to the ~/.ssh/config file, changing thevalues to match your server information:
Each of the following entries describes a feature of the server:
- Host: A shortcut name that you use to tell SSH to use thisconnection.
- HostName: The address of the server to which you connect.
- User: The name of the user account to connect to on theserver.
- IdentityFile: The location of the private key file (id_rsa).
After you set up the config file, connect to the server by usingthe following command with your shortcut name:
Troubleshooting
If you have trouble making a new connection after you restart theserver, use the following steps to help you resolve the issue:
The best way to troubleshoot SSH or SFTP login issues is to attempt tologin through SSH while logged into the Emergency Console and to watch the log,which typically includes the reason for a failure. If no reason is given,it could be a firewall issue. For RPM servers, run the following command to watch the log:
For Debian servers, run the following command to watch the log:
- If you get a
connection timeouterror, check the IP address thatyou used to ensure that it’s correct. You might also check theserver’s iptables to ensure that it isn’t blocking the port used by SSH. - If you get a
connection refusederror, you might be trying to useSSH with the wrong port. If you changed your server to listen to aport other than 22, use the-poption with SSH to specifythe port. - If your login is rejected, then you might have an issuewith your key. Change the
sshdconfiguration to allow passwordconnections by settingPasswordAuthenticationtoyes. Restartthe server and try again. If you connect after these changes, thenthe issue is with the key and you must verify that the key is in theright place on the server. If all else fails, review your changes and restart the SSH daemon onthe server by running the following command:
If you get a message that the SSH service is unknown, run thecommand with
sshdas the service name instead.
Experience what Rackspace has to offer.
©2020 Rackspace US, Inc.
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License
Introduction
SSH (Secure Shell) is a network protocol that enables secure remote connections between two systems. System admins use SSH utilities to manage machines, copy, or move files between systems. Because SSH transmits data over encrypted channels, security is at a high level.
This article will guide you through the most popular SSH commands. The list can also serve as a cheat sheet and will come in handy the next time you need to complete a task.
- An SSH client of your choice
- An SSH server on the remote machine
- The IP address or name of the remote server
To connect to a remote machine, you need its IP address or name. Load the terminal or any SSH client and type ssh followed by the IP address:
or name:
The first time you connect to a host, you’ll see this message:
Type yes and hit enter. You may need to enter your password as well.
SSH uses the current user when accessing a remote server. To specify a user for an SSH connection, run the command in this format:
For instance:
By default, the SSH server listens for a connection on port 22. If the port setting in the SSH config file has been changed, you’ll need to specify the port. Otherwise, you will get this error:
To connect to a remote host with a custom SSH port number, use the -pflag. For example:
To improve the security of SSH connections, generate a key pair with the keygen utility. The pair consists of a public and private key. The public key can be shared, while the private key needs to stay secure.
SSH key pairs are used to authenticate clients to servers automatically. When you create an SSH key pair, there is no longer a need to enter a password to access a server.
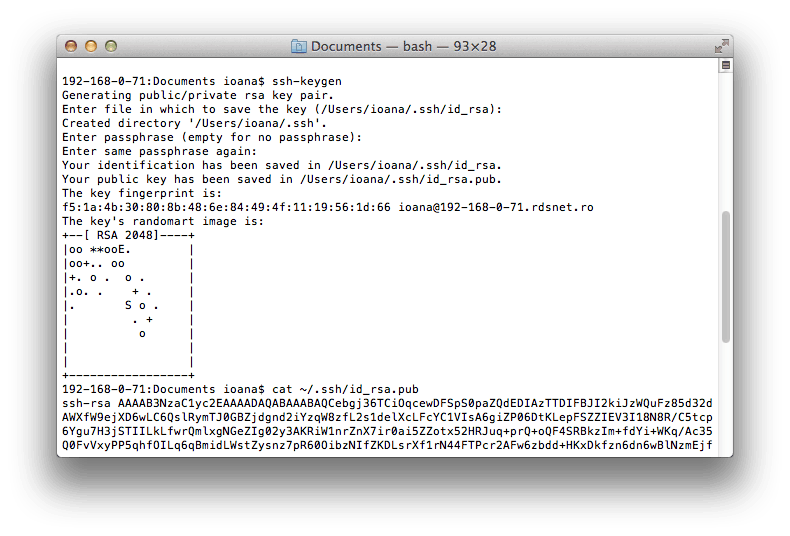
On the host machine’s terminal, use this command to create a key pair:
To use default settings, hit Enter on the prompts for file location and passphrase.
To use the key pair for SSH authentication, you’ll need to copy the public key to a server. The key is the file id_rsa.pub previously created with SSH keygen utility.
To copy your key to a server, run this command from the client:
You can also specify a username if you don’t want to use the current user.
Enter the password to authenticate when asked. After this, you will no longer need to use the password to connect to the same server.
You can securely copy files over the SSH protocol using the SCP tool. The basic syntax is:
For example, to copy a file sample3 to your Desktop on a remote server with a username test, type in:
The output shows a summary of the operation.
Make sure to use the uppercase-Pflag if you need to specify the port.
You can control how remote users can access a server via the SSH. Edit the settings in the sshd_config file to customize SSH server options. Make sure to edit only the options you are familiar with. A server can become inaccessible due to bad configuration.
Command To Generate Ssh Key On Mac Free
Use the editor of your choice to edit the file. You’ll need superuser permissions to make changes. In Linux, we use vim:
In the command line on a remote host, type in:
Enter the sudo password, and the shell opens the file in the editor you used.
When you make changes to the SSH configuration, you’ll need to restart the service in Linux.
Depending on the Linux distro, run one of the following commands on the machine where you modified the settings:
or:
Finally, enter the password to complete the process. As a result, the next SSH session will use the new settings.
Working on a remote server using SSH requires knowing basic SSH commands. Use the commands and options in this article to manage a remote host. Note that you can combine the flags to get the output you need.
Use the pwd command to show the file system path.
The output displays the location of the directory you are in.
To list the contents of a current working folder, use the ls command.
The shell will show the names of all directories, files, and links. To get more information, add one of the following flags:
-adisplays hidden files and entries starting with a dot.-lshows file details for directory contents. For example, the output includes permissions, ownership, date, etc.-slists the size of files, in blocks. Add -h to show the size in a humanly-readable form.
To navigate to a specific folder, use the cd command and a name or path of a directory.
Remember that the names are case sensitive. Use cd without a name or path to return to the user’s home directory.
Useful cd options include:
cd .go to the directory one level higher than your current location.cd -switch to the previous directory.cd /go to the root directory.
Use the cp command to copy a file or directory. You’ll need to include the name of the file and the target location.
To copy file1 from Desktop to Dir1, type in:
To change the name of file1 while copying it to another destination, use this format:
This command copies file1 to Dir1 with a name you specify.
Oct 18, 2019 Generate a Private Key and a CSR If we want to use HTTPS (HTTP over TLS) to secure the Apache or Nginx web servers (using a Certificate Authority (CA) to issue the SSL certificate). Also, the ‘.CSR’ which we will be generating has to be sent to a CA for requesting the certificate for obtaining CA-signed. Generating the Private Key - Linux 1. Open the Terminal. Navigate to the folder with the ListManager directory. Type the following: openssl genrsa -out rsa.private 1024 4. The private key is generated and saved in a file named 'rsa.private' located in the same folder. Generating the Public Key - Linux 1. Open the Terminal. Oct 09, 2019 PKCS#8 files are self-describing, and PKCS#8 private key files contain the public key, so a single command can output all the public properties for any private key. WARNING: By default OpenSSL's command line tool will output the value of the private key, even when you ask for it to output the public metadata; the -noout parameter suppresses this. Openssl generate rsa private key. I'm trying to generate a private RSA key with openssl, which works fine so far. I'd like to get the format of the key in PEM. When writing the key into a file the format seems to be fine but when I save the key in PEM in a char array than it seems to differ from the one written to the file!?
To copy a directory and its contents, use the -r flag in this format:
The mv command works in the same manner as the copy command.
For instance, to move a file to another location, type in:
The touch command allows you to create a new file with any extension.
In the terminal, enter the following command:
For example, to create a system.log file, type in:
Ssh Key Generator Mac
To create a directory, use the mkdir command. Enter a new directory name or full path in this format:
Or:
To delete a Linux file , use rm in this format:
In addition, you can enter a full path:
To delete a directory, add the -r flag to the rm command.
To view the status of all network adapters, use the ifconfig command. Moreover, when you don’t use any options with ifconfig, the output displays only active interfaces.
To clear the current working area of your bash screen, type clear in the shell. This command clears one portion of the screen and shifts up the previous output.
To remove the output from the terminal completely, use the reset command.
Run a Command on a Remote Server from a Local Computer
This method does not create a new shell. Instead, it runs a command and returns the user to the local prompt. You can create a file, copy files, or run any other SSH command in this format.
To remotely execute a command from the local machine, append an instruction to the SSH command. For example, to delete a file, type in:
Enter the password, and the file on the remote server will be deleted without creating a new shell.
The SSH tool comes with many optional parameters. The table below lists common SSH options and the corresponding descriptions.
| SSH Option | Description |
| -1 | Instructs ssh to use protocol version 1 |
| -2 | Instructs ssh to use protocol version 2. |
| -4 | Permits only IPv4 addresses. |
| -6 | Permits only IPv6 addresses. |
| -A | Enables authentication agent connection forwarding. Use this option with caution. |
| -a | Disables authentication agent connection forwarding. |
| -b bind_address | Use this option on the local host with more than one address to set the source address of the connection. |
| -C | Enables data compression for all files. Only to be used with slow connections. |
| -c cipher_spec | Use to select a cipher specification. List the values separated by a comma. |
| -E log_fileName | Attaches debug logs to log_file instead of standard error. |
| -f | Sends ssh to background, even before entering a password or passphrase. |
| -g | Permits remote hosts to connect to ports forwarded on a local machine. |
| -q | Runs ssh in quiet mode. It suppresses most error or warning messages. |
| -V | Displays the version of ssh tool and exits. |
| -v | Prints debugging messages for ssh connection. The verbose mode is useful when troubleshooting configuration issues. |
| -X | Use this option to enable X11 forwarding. |
| -x | Disable X11 forwarding. |
This article has covered the 19 most popular commands for using the SSH tool effectively. Now you can manage your server remotely with an added layer of security and have these commands at your fingertips.
Before executing these commands and options on a live server, we do recommend using a test machine first.
Next you should also read
Mac Ssh Key Location
The article covers the 5 most common and efficient ways to secure an SSH connection. The listed solutions go…
This article provides all the information you need in order to set up SSH encryption on your remote device.…
If you are using Debian 9 or Debian 10 to manage servers, you must ensure that the transfer of data is as…
How To Generate Ssh Key On Mac
When establishing a remote connection between a client and a server, a primary concern is ensuring a secure…
Command To Generate Ssh Key On Mac Download
MySQL is an open-source relational database server tool for Linux operating systems. It is widely used in…