Before you begin
Using SSH public-key authentication to connect to a remote system is a robust, more secure alternative to logging in with an account password or passphrase. SSH public-key authentication relies on asymmetric cryptographic algorithms that generate a pair of separate keys (a key pair), one 'private' and the other 'public'. You keep the private key a secret and store it on the computer you use to connect to the remote system. Conceivably, you can share the public key with anyone without compromising the private key; you store it on the remote system in a .ssh/authorized_keys directory.
To use SSH public-key authentication:
- The remote system must have a version of SSH installed. The information in this document assumes the remote system uses OpenSSH. If the remote system is using a different version of SSH (for example, Tectia SSH), the process outlined below may not be correct.
- The computer you use to connect to the remote server must have a version of SSH installed. This document includes instructions for generating a key pair with command-line SSH on a Linux or macOS computer, and with PuTTY on a Windows computer.
- You need to be able to transfer your public key to the remote system. Therefore, you must either be able to log into the remote system with an established account username and password/passphrase, or have an administrator on the remote system add the public key to the
~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile in your account. - Two-factor authentication using Two-Step Login (Duo) is required for access to the login nodes on IU research supercomputers, and for SCP and SFTP file transfers to those systems. SSH public-key authentication remains an option for researchers who submit the 'SSH public-key authentication to HPS systems' user agreement (log into HPC everywhere using your IU username and passphrase), in which you agree to set a passphrase on your private key when you generate your key pair. If you have questions about how two-factor authentication may impact your workflows, contact the UITS Research Applications and Deep Learning team. For help, see Get started with Two-Step Login (Duo) at IU and Help for Two-Step Login (Duo).
Set up public-key authentication using SSH on a Linux or macOS computer
To set up public-key authentication using SSH on a Linux or macOS computer:
- Mar 31, 2018 In this post I will demonstrate how to regenerate a public key from the corresponding private key that you still have. Generate public key and store into a file. It is a simple one liner command to generate a public key from a private key, so lets say our private key is named ‘[email protected]’ and we want to generate the public key.
- Mar 28, 2018 Generating RSA-SSH Public Key, OpenSSH & PuTTY Compatible Private Keys using PuTTYgen. In a consideration of security, most of the remote SSH connectivity are now transforming to Password-less RSA Authentication. Basically in this method, authentication is being done on the basis of Private / Public key. In which, Server will have a Public Key.
- Generate online private and public key for ssh, putty, github, bitbucket Save both of keys on your computer (text file, dropbox, evernote etc)!!! The generated keys are RANDOM and CAN'T be restored.
- Here's how you can generate SSH public/private keys on Windows. The newer release of Windows 10 includes an OpenSSH client out of the box. Here's how you can generate SSH public/private keys on Windows. Generate Public/Private SSH Key Pair. Open Command Prompt from the.
Please do NOT click on ‘save public key’, as Puttygen uses a different format to OpenSSH. Thankfully, Puttygen does display the OpenSSH-compatible public key in the field labeled ‘Public key for pasting into OpenSSH’. Select all the text in this field and copy it to clipboard. Go back to the CloudSigma SSH key screen and paste this into.
- Log into the computer you'll use to access the remote host, and then use command-line SSH to generate a key pair using the RSA algorithm.
To generate RSA keys, on the command line, enter:
- You will be prompted to supply a filename (for saving the key pair) and a password (for protecting your private key):
- Filename: To accept the default filename (and location) for your key pair, press
EnterorReturnwithout entering a filename.Alternatively, you can enter a filename (for example,
my_ssh_key) at the prompt, and then pressEnterorReturn. However, many remote hosts are configured to accept private keys with the default filename and path (~/.ssh/id_rsafor RSA keys) by default. Consequently, to authenticate with a private key that has a different filename, or one that is not stored in the default location, you must explicitly invoke it either on the SSH command line or in an SSH client configuration file (~/.ssh/config); see below for instructions. - Password: Enter a password that contains at least five characters, and then press
EnterorReturn. If you pressEnterorReturnwithout entering a password, your private key will be generated without password-protection.If you don't password-protect your private key, anyone with access to your computer conceivably can SSH (without being prompted for a password) to your account on any remote system that has the corresponding public key.
Your private key will be generated using the default filename (for example,
id_rsa) or the filename you specified (for example,my_ssh_key), and stored on your computer in a.sshdirectory off your home directory (for example,~/.ssh/id_rsaor~/.ssh/my_ssh_key).The corresponding public key will be generated using the same filename (but with a
.pubextension added) and stored in the same location (for example,~/.ssh/id_rsa.pubor~/.ssh/my_ssh_key.pub). - Filename: To accept the default filename (and location) for your key pair, press
- Use SFTP or SCP to copy the public key file (for example,
~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub) to your account on the remote system (for example,[email protected]); for example, using command-line SCP:Windows server 2008 r2 activation key generator. You'll be prompted for your account password. Your public key will be copied to your home directory (and saved with the same filename) on the remote system.
- Log into the remote system using your account username and password.If the remote system is not configured to support password-based authentication, you will need to ask system administrators to add your public key to the
~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile in your account (if your account doesn't have~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile, system administrators can create one for you). Once your public key is added to your~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile on the remote system, the setup process is complete, and you should now be able to SSH to your account from the computer that has your private key. - If your account on the remote system doesn't already contain a
~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile, create one; on the command line, enter the following commands:If your account on the remote system already has a~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile, executing these commands will not damage the existing directory or file. - On the remote system, add the contents of your public key file (for example,
~/id_rsa.pub) to a new line in your~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile; on the command line, enter:You may want to check the contents of
~/.ssh/authorized_keysto make sure your public key was added properly; on the command line, enter: - You may now safely delete the public key file (for example,
~/id_rsa.pub) from your account on the remote system; on the command line, enter:Alternatively, if you prefer to keep a copy of your public key on the remote system, move it to your
.sshdirectory; on the command line, enter: - Optionally, repeat steps 3-7 to add your public key to other remote systems that you want to access from the computer that has your private key using SSH public-key authentication.
- You now should be able to SSH to your account on the remote system (for example,
[email protected]) from the computer (for example,host1) that has your private key (for example,~/.ssh/id_rsa):- If your private key is password-protected, the remote system will prompt you for the password or passphrase (your private key password/passphrase is not transmitted to the remote system):
- If your private key is not password-protected, the remote system will place you on the command line in your home directory without prompting you for a password or passphrase:
If the private key you're using does not have the default name, or is not stored in the default path (not
~/.ssh/id_rsa), you must explicitly invoke it in one of two ways:- On the SSH command line: Add the
-iflag and the path to your private key.For example, to invoke the private key
host2_key, stored in the~/.ssh/old_keysdirectory, when connecting to your account on a remote host (for example,[email protected]), enter: - In an SSH client configuration file: SSH gets configuration data from the following sources (in this order):
- From command-line options
- From the user's client configuration file (
~/.ssh/config), if it exists - From the system-wide client configuration file (
/etc/ssh/ssh_config)
The SSH client configuration file is a text file containing keywords and arguments. To specify which private key should be used for connections to a particular remote host, use a text editor to create a
~/.ssh/configthat includes theHostandIdentityFilekeywords.For example, for connections to
host2.somewhere.edu, to make SSH automatically invoke the private keyhost2_key, stored in the~/.ssh/old_keysdirectory, create a~/.ssh/configfile with these lines included:Once you save the file, SSH will use the specified private key for future connections to that host.
You can add multiple
HostandIdentityFiledirectives to specify a different private key for each host listed; for example:Alternatively, you can use a single asterisk (
*) to provide global defaults for all hosts (specify one private key for several hosts); for example:For more about the SSH client configuration file, see the OpenSSH SSH client configuration file on the web or from the command line (
man ssh_config).
Set up public-key authentication using PuTTY on a Windows 10 or Windows 8.x computer
The PuTTY command-line SSH client, the PuTTYgen key generation utility, the Pageant SSH authentication agent, and the PuTTY SCP and SFTP utilities are packaged together in a Windows installer available under The MIT License for free download from the PuTTY development team.
After installing PuTTY:
- Launch PuTTYgen.
- In the 'PuTTY Key Generator' window, under 'Parameters':
- For 'Type of key to generate', select RSA. (In older versions of PuTTYgen, select SSH2-RSA.)
- For 'Number of bits in a generated key', leave the default value (
2048).
- Under 'Actions', click Generate.
- When prompted, use your mouse (or trackpad) to move your cursor around the blank area under 'Key'; this generates randomness that PuTTYgen uses to generate your key pair.
- When your key pair is generated, PuTTYgen displays the public key in the area under 'Key'. In the 'Key passphrase' and 'Confirm passphrase' text boxes, enter a passphrase to passphrase-protect your private key.If you don't passphrase-protect your private key, anyone with access to your computer will be able to SSH (without being prompted for a passphrase) to your account on any remote system that has the corresponding public key.
- Save your public key:
- Under 'Actions', next to 'Save the generated key', click Save public key.
- Give the file a name (for example,
putty_key), select a location on your computer to store it, and then click Save.
- Save your private key:
- Under 'Actions', next to 'Save the generated key', click Save private key.If you didn't passphrase-protect your private key, the utility will ask whether you're sure you want to save it without a passphrase. Click Yes to proceed or No to go back and create a passphrase for your private key.
- Keep 'Save as type' set to PuTTY Private Key Files (*.ppk), give the file a name (for example,
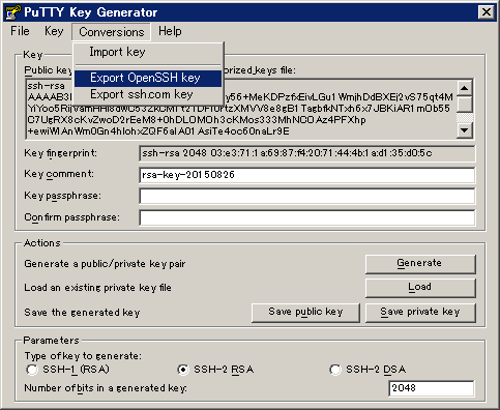
putty_private_key), select a location on your computer to store it, and then click Save. - If you wish to connect to a remote desktop system such as Research Desktop (RED), click Conversions > Export OpenSSH key, give the file a name (for example,
putty_rsa), select a location on your computer to store it, and then click Save.
- Under 'Actions', next to 'Save the generated key', click Save private key.
- Log into the remote system using your account username and password.
If the remote system does not support password-based authentication, you will need to ask system administrators to add your public key to the
~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile in your account (if your account doesn't have~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile, system administrators can create one for you). Once your public key is added to your account's~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile on the remote system.. - If your account on the remote system doesn't already contain a
~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile, create one; on the command line, enter the following commands:If your account on the remote system already has
~/.ssh/authorized_keys, executing these commands will not damage the existing directory or file. - On your computer, in the PuTTYgen utility, copy the contents of the public key (displayed in the area under 'Key') onto your Clipboard. Then, on the remote system, use your favorite text editor to paste it onto a new line in your
~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile, and then save and close the file. - On your computer, open the Pageant SSH authentication agent. This utility runs in the background, so when it opens, you should see its icon displayed in the Windows notification area.
- In the Windows notification area, right-click on the Pageant icon, select Add Key, navigate to the location where you saved your private key (for example,
putty_private_key.ppk), select the file, and then click Open. - If your private key is passphrase-protected, Pageant will prompt you to enter the passphrase; enter the passphrase for your private key, and then click OK.
If your private key is not passphrase-protected, Pageant will add your private key without prompting you for a passphrase.
Either way, Pageant stores the unencrypted private key in memory for use by PuTTY when you initiate an SSH session to the remote system that has your public key.
- On your computer, open the PuTTY SSH client:
- On the Session screen:
- Under 'Host Name (or IP address)', enter your username coupled with the hostname of the remote server that has your public key; for example:
- Under 'Connection type', make sure SSH is selected.
- In the 'Category' list on the left, navigate to the Auth screen (Connection > SSH > Auth). On the Auth screen, under 'Authentication methods', select Attempt authentication using Pageant.
- Return to the Session screen, and under 'Saved Sessions', enter a name (for example,
Deathstar), and then click Save. - Click Open to connect to your account on the remote system. With Pageant running in the background, PuTTY will retrieve the unencrypted private key automatically from Pageant and use it to authenticate. Because Pageant has your private key's passphrase saved (if applicable), the remote system will place you on the command line in your account without prompting you for the passphrase.
Technically, at this point, the setup is complete. In the future, whenever you log into your Windows desktop, you can run Pageant, add the private key, and then use PuTTY to SSH to any remote resource that has your public key. Alternatively, you can create a shortcut in your WindowsStartupfolder to launch Pageant and load your private key automatically whenever you log into your desktop. For instructions, finish the rest of the following steps. - On the Session screen:
- Open your
Startupfolder. PressWin-r, and in the 'Open' field, typeshell:startup, and then pressEnter. - Right-click inside the
Startupfolder, and then select New and Shortcut. - In the 'Type the location of the item' text box, enter the path to the Pageant executable (
pageant.exe) followed by the path to your private key file (for example,putty_private_key.ppk); enclose both paths in double quotes; for example: - Click Next, and then, in the 'Type a name for this shortcut' text box, enter a name for the shortcut (for example,
PAGEANT). - Click Finish.
The next time you log into your Windows desktop, Pageant will start automatically, load your private key, and (if applicable) prompt you for the passphrase.
- This module allows one to (re)generate OpenSSH private and public keys. It uses ssh-keygen to generate keys. One can generate
rsa,dsa,rsa1,ed25519orecdsaprivate keys.
The below requirements are needed on the host that executes this module.
- ssh-keygen
| Parameter | Choices/Defaults | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| attributes string | The attributes the resulting file or directory should have. To get supported flags look at the man page for chattr on the target system. This string should contain the attributes in the same order as the one displayed by lsattr. The = operator is assumed as default, otherwise + or - operators need to be included in the string. | |
| comment added in 2.9 | Provides a new comment to the public key. When checking if the key is in the correct state this will be ignored. | |
| force boolean |
| Should the key be regenerated even if it already exists |
| group string | Name of the group that should own the file/directory, as would be fed to chown. | |
| mode string | The permissions the resulting file or directory should have. For those used to /usr/bin/chmod remember that modes are actually octal numbers. You must either add a leading zero so that Ansible's YAML parser knows it is an octal number (like 0644 or 01777) or quote it (like '644' or '1777') so Ansible receives a string and can do its own conversion from string into number.Giving Ansible a number without following one of these rules will end up with a decimal number which will have unexpected results. As of Ansible 1.8, the mode may be specified as a symbolic mode (for example, u+rwx or u=rw,g=r,o=r).As of Ansible 2.6, the mode may also be the special string preserve.When set to preserve the file will be given the same permissions as the source file. | |
| owner string | Name of the user that should own the file/directory, as would be fed to chown. | |
| path path / required | Name of the files containing the public and private key. The file containing the public key will have the extension .pub. | |
| selevel string | Default: | The level part of the SELinux file context. This is the MLS/MCS attribute, sometimes known as the range.When set to _default, it will use the level portion of the policy if available. |
| serole string | When set to _default, it will use the role portion of the policy if available. | |
| setype string | When set to _default, it will use the type portion of the policy if available. | |
| seuser string | By default it uses the system policy, where applicable.When set to _default, it will use the user portion of the policy if available. | |
| size integer | Specifies the number of bits in the private key to create. For RSA keys, the minimum size is 1024 bits and the default is 4096 bits. Generally, 2048 bits is considered sufficient. DSA keys must be exactly 1024 bits as specified by FIPS 186-2. For ECDSA keys, size determines the key length by selecting from one of three elliptic curve sizes: 256, 384 or 521 bits. Attempting to use bit lengths other than these three values for ECDSA keys will cause this module to fail. Ed25519 keys have a fixed length and the size will be ignored. | |
| state string |
| Whether the private and public keys should exist or not, taking action if the state is different from what is stated. |
| type string |
| The algorithm used to generate the SSH private key. rsa1 is for protocol version 1. rsa1 is deprecated and may not be supported by every version of ssh-keygen. |
| unsafe_writes boolean |
| Influence when to use atomic operation to prevent data corruption or inconsistent reads from the target file. By default this module uses atomic operations to prevent data corruption or inconsistent reads from the target files, but sometimes systems are configured or just broken in ways that prevent this. One example is docker mounted files, which cannot be updated atomically from inside the container and can only be written in an unsafe manner. This option allows Ansible to fall back to unsafe methods of updating files when atomic operations fail (however, it doesn't force Ansible to perform unsafe writes). IMPORTANT! Unsafe writes are subject to race conditions and can lead to data corruption. |
Generate A Public Key From A Private Key Openssh File
Common return values are documented here, the following are the fields unique to this module:
| Key | Returned | Description |
|---|---|---|
| comment string | changed or success | Sample: |
| filename | changed or success | Path to the generated SSH private key file /tmp/id_ssh_rsa |
| fingerprint string | changed or success | Sample: SHA256:r4YCZxihVjedH2OlfjVGI6Y5xAYtdCwk8VxKyzVyYfM |
| public_key string | changed or success | Sample: ssh-rsa AAAAB3Nza(..omitted..)veL4E3Xcw test_key |
| size integer | changed or success | Sample: |
| type | changed or success | Algorithm used to generate the SSH private key rsa |
- This module is not guaranteed to have a backwards compatible interface. [preview]
- This module is maintained by the Ansible Community. [community]
Authors¶
- David Kainz (@lolcube)
Hint
If you notice any issues in this documentation, you can edit this document to improve it.