Scientists look at half-life decay rates of radioactive isotopes to estimate when a particular atom might decay. A useful application of half-lives is radioactive dating. This has to do with figuring out the age of ancient things.
If you could watch a single atom of a radioactive isotope, U-238, for example, you wouldn’t be able to predict when that particular atom might decay. It might take a millisecond, or it might take a century. There’s simply no way to tell.
I am trying to create a list of exponential decay of fix length with a predetermine half-life as efficiently as possible. So assuming I want I half-life of 1 and a list length of 5 it would retu. And Mme Curie subjected a large amount of pitchblende to a laborious process of fractionation, with the result that in 1898 they announced the existence in it of. Modify your STELLA program to graph λ 1 N 1 and λ 2 N 2 over time, and then set the half-life of the parent to 1 hour and that of the radioactive daughter to 10 hours. Run your model for about 10 hours. The half-life of a radioactive isotope refers to the amount of time required for half of a quantity of a radioactive isotope to decay. Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5,730 years, which means that if you take one gram of carbon-14, half of it will decay in 5,730 years. Nov 28, 2012 Half-life is the time it takes for half of a sample of an element to decay. For example, I have eight Francium-223 atoms. Francium-223 has a half life of about 22 minutes. This means that in 22 minutes, half of those Francium atoms will have decayed (for you math people, that is four).
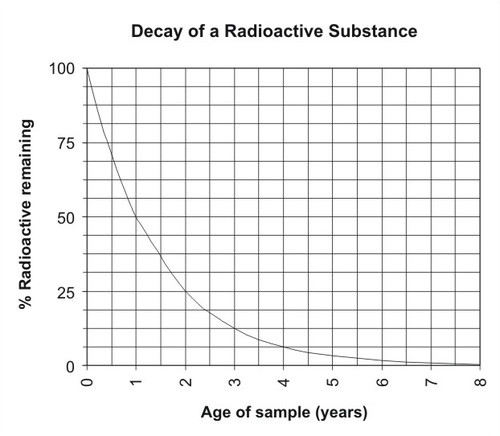
But if you have a large enough sample, a pattern begins to emerge. It takes a certain amount of time for half the atoms in a sample to decay. It then takes the same amount of time for half the remaining radioactive atoms to decay, and the same amount of time for half of those remaining radioactive atoms to decay, and so on. This process is shown in the following table.
| Half-Life | Percent of Radioactive Isotope Remaining |
|---|---|
| 0 | 100.00 |
| 1 | 50.00 |
| 2 | 25.00 |
| 3 | 12.50 |
| 4 | 6.25 |
| 5 | 3.12 |
| 6 | 1.56 |
| 7 | 0.78 |
| 8 | 0.39 |
| 9 | 0.19 |
| 10 | 0.09 |
The amount of time it takes for one-half of a sample to decay is called the half-life of the isotope, and it’s given the symbol:
It’s important to realize that the half-life decay of radioactive isotopes is not linear. For example, you can’t find the remaining amount of an isotope as 7.5 half-lives by finding the midpoint between 7 and 8 half-lives. This decay is an example of an exponential decay, shown in the figure below.
Safe handling of radioactive material
Knowing about half-lives is important because it enables you to determine when a sample of radioactive material is safe to handle. The rule is that a sample is safe when its radioactivity has dropped below detection limits. And that occurs at 10 half-lives.
So, if radioactive iodine-131 (which has a half-life of 8 days) is injected into the body to treat thyroid cancer, it’ll be “gone” in 10 half-lives, or 80 days.
This stuff is important to know when using radioactive isotopes as medical tracers, which are taken into the body to allow doctors to trace a pathway or find a blockage, or in cancer treatments. They need to be active long enough to treat the condition, but they should also have a short enough half-life so that they don’t injure healthy cells and organs.
Radioactive dating
Radioactive dating is helpful for figuring out the age of ancient things. Carbon-14 (C-14), a radioactive isotope of carbon, is produced in the upper atmosphere by cosmic radiation. The primary carbon-containing compound in the atmosphere is carbon dioxide, and a very small amount of carbon dioxide contains C-14.
Plants absorb C-14 during photosynthesis, so C-14 is incorporated into the cellular structure of plants. Plants are then eaten by animals, making C-14 a part of the cellular structure of all living things.
Radioactive Half-life Chart
As long as an organism is alive, the amount of C-14 in its cellular structure remains constant. But when the organism dies, the amount of C-14 begins to decrease. Scientists know the half-life of C-14 (5,730 years), so they can figure out how long ago the organism died.
To sign an assembly with a strong name, you must have a public/private key pair. This public and private cryptographic key pair is used during compilation to create a strong-named assembly. You can create a key pair using the Strong Name tool (Sn.exe). Key pair files. Depends on the algorithm. With RSA, you cannot, with EC you can. However, the public key is usually always stored together with the private key (not the other way around, though, of course), so this is not really a problem (if you have the private key, the same file also includes the public key). A public key/private key keypair, is generated by using special programs according to the use of the keypair. If it’s ssh, it is described in other answers. If it’s a cryptocurrency keypair, every cryptocurrency has it’s own software to do this. Public key definition. Most of the computer cloud (VPS) providers today give you an easy way to add your public key(s) through their web interface control panels. Once you start a server with this associated public key, you will be able to log in with your private key. To generate the missing public key again from the private key, the following command will generate the public key of the private key provided with the -f option. $ ssh-keygen -y -f /.ssh/idrsa /.ssh/idrsa.pub Enter passphrase: The -y option will read a private SSH key file and prints an SSH public key to stdout. The public key part is.
Using Radioactive Half Life To Generate Keys Lyrics
Carbon-14 dating can only be used to determine the age of something that was once alive. It can’t be used to determine the age of a moon rock or a meteorite. For nonliving substances, scientists use other isotopes, such as potassium-40.