[TOC]
Create and add your SSH public key. It is best practice to use Git over SSH instead of Git over HTTP. In order to use SSH, you will need to: Create an SSH key pair on your local computer. Add the key to GitLab. Go to your command line. Follow the instructions to generate your SSH key pair. You have to generate ssh key first and submit this key to your account in github or bitbucket, we are going to see how to generate this key either for windows 7, 8 or 10.
Overview
OSG Connect requires SSH-key-based logins. You need to followa two-step process to set up the SSH key to your account.
Generate a SSH key pair.
Add your public key to the submit host by uploading it toyour OSG Connect user profile (via the OSG Connect website).
After completing the process, you can log in from a local computer(your laptop or desktop) to the OSG Connect login node assignedusing either ssh or an ssh program like Putty -- see below formore details on logging in.

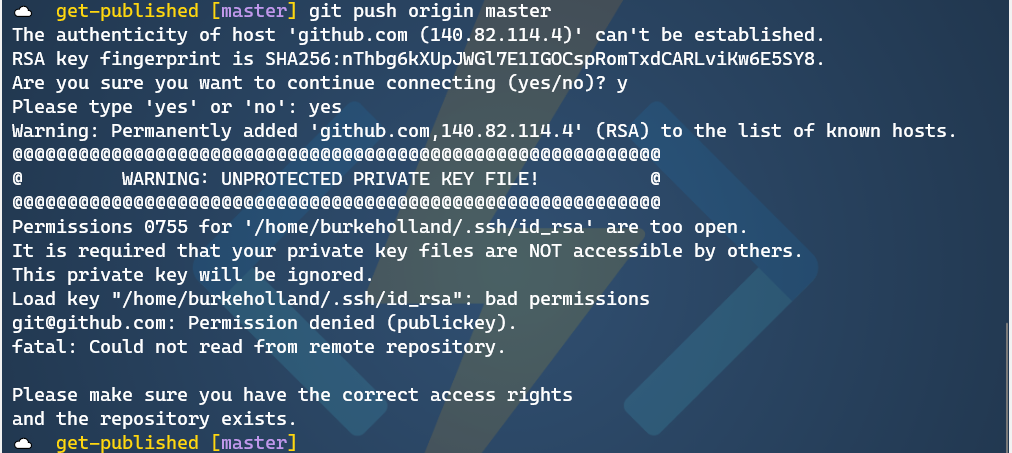
NOTE: Please do not edit the authorized keys file on the login node.
Step 1: Generate SSH Keys
We will discuss how to generate a SSH key pair for two cases:
- 'Unix' systems (Linux, Mac) and certain, latest versions of Windows
- Older Windows systems
Generate Ssh Key Windows 10 Github Free
Please note: The key pair consist of a private key and a public key. You will upload thepublic key to OSG Connect, but you also need to keep a copy of the private key to log in!
You should keep the private key on machines that you havedirect access to, i.e. your local computer (your laptop or desktop).
Unix-based operating system (Linux/Mac) or latest Windows 10 versions
Open a terminal on your local computer and run the following commands:
The last command will produce a prompt similar to
Unless you want to change the location of the key, continue by pressing enter.Now you will be asked for a passphrase. Enter a passphrase that you will beable to remember and which is secure:
When everything has successfully completed, the output should resemble thefollowing:
The part you want to upload is the content of the .pub file (~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub)
Windows, using Putty to log in
If you can connect using the ssh command within the Command Prompt (Windows 10 build version 1803 and later), please follow the Mac/Linux directions above. If not,continue with the directions below.
Open the
PuTTYgenprogram. You can downloadPuttyGenhere: PuttyGen Download Page,scroll down until you see theputtygen.exefile.For Type of key to generate, select RSA or SSH-2 RSA.
Click the 'Generate' button.
Move your mouse in the area below the progress bar.When the progress bar is full, PuTTYgen generates your key pair.
Generate 512 characters auth secret key in terminal 2. Exporting and Re-Importing a KeyNext, export the secret key to a file mykey.asc to gpg (using the key holder’s name, email or key ID): $ gpg -armor -export-secret-keys Cosmo Kramer mykey.ascYou can now, on a different machine, re-import the key, but you will also have to trust it again. You can pass the full name in quotes or the e-mail to gpg and it will pick the right one. I highly recommend you pick a pass phrase!You can verify it is loaded into your system’s keychain by running:M-x epa-list-secret-keys in Emacs;or gpg -list-secret-keys on your command line, in which case it’ll look like this: $ gpg -list-secret-keyssec 2048R/5DB69AC1 2016-06-13uid Cosmo Kramer (Kramerica Industries) ssb 2048R/02A-06-13or using a UI program like seahorse. Creating a keyTo get started you must first generate the key pair with gpg: $ gpg -gen-keyFollow the prompts to generate your key. The benefit of the key is that you can keep it loaded into memory and let Emacs decrypt and re-encrypt files without prompting you for a password.
Type a passphrase in the 'Key passphrase' field. Type the same passphrase in the 'Confirm passphrase' field. Youcan use a key without a passphrase, but this is not recommended.
Click the 'Save private key' button to save the private key. You must save the private key. You will need it to connect to your machine.
Right-click in the text field labeled 'Public key for pasting into OpenSSH authorized_keys file' and choose Select All.
Right-click again in the same text field and choose Copy.
Step 2: Add the public SSH key to login node
To add your public key to the OSG Connect log in node:
Go to www.osgconnect.net and sign in with the institutional identity you used when requesting an OSG Connect account.
Click 'Profile' in the top right corner.
Click the 'Edit Profile' button located after the user information in the left hand box.
Copy/paste the public key which is found in the
.pubfile into the 'SSH Public Key' text box.The expected key is a single line, with three fields looking something likessh-rsa ASSFFSAF.. user@host. If you used the first set of key-generatinginstructions it is the content of~/.ssh/id_rsa.puband for the second (usingPuTTYgen), it is the content from step 7 above.Click 'Update Profile'
The key is now added to your profile in the OSG Connect website. This will automaticallybe added to the login nodes within a couple hours.
Logging In
After following the steps above to upload your key and it's been a few hours, you shouldbe able to log in to OSG Connect.
Determine which login node to use
Before you can connect, you will need to know which login node your account is assigned to. You can findthis information on your profile from the OSG Connect website.
Go to www.osgconnect.net and sign in with your CILogin.
Click 'Profile' in the top right corner.
The assigned login nodes are listed in the left side box. Make note of the address ofyour assigned login node as you will use this to connect to OSG Connect.
For Mac, Linux, or newer versions of Windows
Open a terminal and type in:
It will ask for the passphrase for your ssh key (if you set one) and then youshould be logged in.
For older versions of Windows
On older versions of Windows, you can use the Putty program to log in.
Open the
PutTTYprogram. If necessary, you can download PuTTY from the website here PuTTY download page.Type the address of your assigned login node as the hostname (see 'Determine which login node to use' above).
In the left hand menu, click the '+' next to 'SSH' to expand the menu.
Click 'Auth' in the 'SSH' menu.
Click 'Browse' and specify the private key file you saved in step 5 above.
Click 'Open' and provide your passphrase when prompted to do so.
Getting Help
For assistance or questions, please email the OSG User Support team at mailto:[email protected] or visit the help desk and community forums.