SSL Certificates fall into two broad categories: 1) Self-Signed Certificate which is an identity certificate that is signed by the same entity whose identity it certifies-on signed with its own private key, and 2) Certificates that are signed by a CA (Certificate Authority) such as Let’s Encrypt, Comodo and many other companies.
Looking for Tableau Server on Linux? See Example: SSL Certificate - Generate a Key and CSR. Tableau Server uses Apache, which includes OpenSSL. You can use the OpenSSL toolkit to generate a key file and Certificate Signing Request (CSR) which can then be used to obtain a signed SSL certificate. Steps to generate a key and CSR.
Self-Signed Certificates are commonly used in test environments for LAN services or applications. They can be generated for free using OpenSSL or any related tool. On the other hand, for sensitive, public-facing production services, applications or websites, it is highly recommended to use a certificate issued and verified by a trusted CA.
The first step towards acquiring an SSL certificate issued and verified by a CA is generating a CSR (short for Certificate Signing Request).
In this article, we will demonstrate how to create a CSR (Certificate Signing Request) on a Linux system.
Creating a CSR – Certificate Signing Request in Linux
Linux Generate Ssl Key And Certificate Code
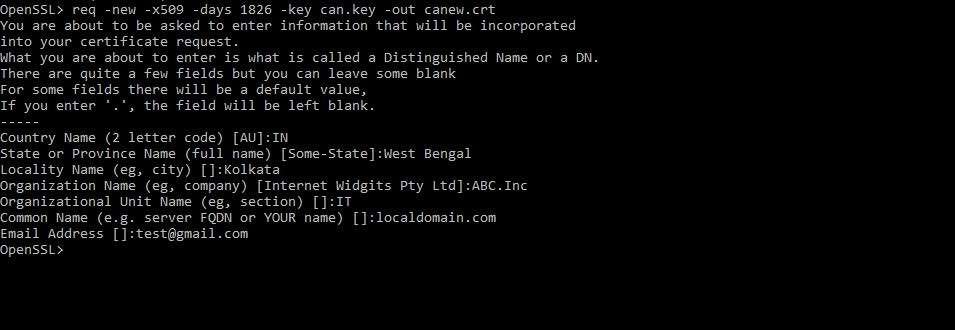
To create a CSR, you need the OpenSSL command line utility installed on your system, otherwise, run the following command to install it.
Linux Generate Certificate
Then issue the following command to generate a CSR and the key that will protect your certificate.
where:
- req enables the part of OpenSSL that handles certificate requests signing.
- -newkey rsa:2048 creates a 2048-bit RSA key.
- -nodes means “don’t encrypt the key”.
- -keyout example.com.key specifies the filename to write on the created private key.
- -out example.com.csr specifies the filename to write the CSR to.
Answer correctly, the questions you will be asked. Note that your answers should match information in legal documents regarding the registration of your company. This information is critically checked by the CA before issuing your certificate.
After creating your CSR, view the contents of the file using a cat utility, select it and copy it.
Copy CSR Key
Then go back to your CA’s website, log in, go to the page will contain the SSL certificate you purchased, and activate it. Then in a window such as the one below, paste your CSR in the correct input field.
In this example, we created a CSR for a multiple domain certificate purchased from Namecheap.
Then follow the rest of the instructions to initiate activation of your SSL certificate. For more information about OpenSSL command, see its man page:
That’s all for now! Always remember that the first step to getting your own SSL certificate from a CA is to generate a CSR. Use the feedback form below to ask any questions or share your comments with us.
If you want to convert your website from HTTP to HTTPS, you need to get a SSL certificate from a valid organization like Verisign or Thawte. You can also generate self signed SSL certificate for testing purpose.
In this article, let us review how to generate private key file (server.key), certificate signing request file (server.csr) and webserver certificate file (server.crt) that can be used on Apache server with mod_ssl.
Key, CSR and CRT File Naming Convention
I typically like to name the files with the domain name of the HTTPS URL that will be using this certificate. This makes it easier to identify and maintain.
- Instead of server.key, I use www.thegeekstuff.com.key
- Instead of server.csr, I use www.thegeekstuff.com.csr
- Instead of server.crt, I use www.thegeekstuff.com.crt
1. Generate Private Key on the Server Running Apache + mod_ssl
First, generate a private key on the Linux server that runs Apache webserver using openssl command as shown below.
The generated private key looks like the following.
2. Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
Myscript notes 2.1 key generator. Using the key generate above, you should generate a certificate request file (csr) using openssl as shown below.
3. Generate a Self-Signed SSL Certificate
For testing purpose, you can generate a self-signed SSL certificate that is valid for 1 year using openssl command as shown below.
You can use this method to generate Apache SSL Key, CSR and CRT file in most of the Linux, Unix systems including Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, Fedora and Red Hat.
4. Get a Valid Trial SSL Certificate (Optional)
Instead of signing it youself, you can also generate a valid trial SSL certificate from thawte. i.e Before spending the money on purchasing a certificate, you can also get a valid fully functional 21 day trial SSL certificates from Thawte. Once this valid certificate works, you can either decide to purchase it from Thawte or any other SSL signing organization.
This step is optional and not really required. For testing purpose, you can always use the self-signed certificate that was generated from the above step.
Go to Thwate trial certificate request page and do the following:
- Select “SSL Web Server Certificate (All servers)” under the “select your trial certificate”.
- Do not check the PKCS #7 check-box under the “configure certificate”
- Copy/Paste the *.csr file that you generate above in the textbox under “certificate signing request (CSR)”
- Click on next at the bottom, which will give you a 21-day free trial certificate.
Copy/Paste the trial certificate to the www.thegeekstuff.com.crt file as shown below.
If you enjoyed this article, you might also like.
Next post: Google Chrome OS – Beginning of End of Microsoft?
Previous post: Blog Makeover: New Thesis Theme In Action